




Author: Dr. Garima Bishwas
Yoga 0
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is one of the most common nerve-related conditions, affecting millions of individuals globally. Whether you're typing at your desk, performing yoga postures, or carrying a child during pregnancy, your wrists endure more stress than you may realize. When the pressure becomes too much on a specific nerve in your wrist, it can lead to a painful and persistent condition known as carpal tunnel syndrome.
Understanding what it is, the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, and the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome is essential for early intervention and effective management. Let’s explore everything you need to know about this condition.
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition that occurs when the median nerve-one of the main nerves in the hand-gets compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel, a narrow passageway in the wrist.
1. Anatomy of the Carpal Tunnel
The carpal tunnel is a rigid, narrow channel made of bones and ligaments located at the base of your hand. Inside this tunnel runs the median nerve along with tendons that help you bend your fingers. Any swelling or inflammation in this area can compress the median nerve, leading to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
2. Nerve Compression and Its Impact
When the median nerve is compressed, it affects sensation and movement in the thumb, index, and middle fingers. This is why carpal tunnel syndrome often presents with tingling, numbness, and even pain. If left untreated, this condition can lead to permanent nerve damage.
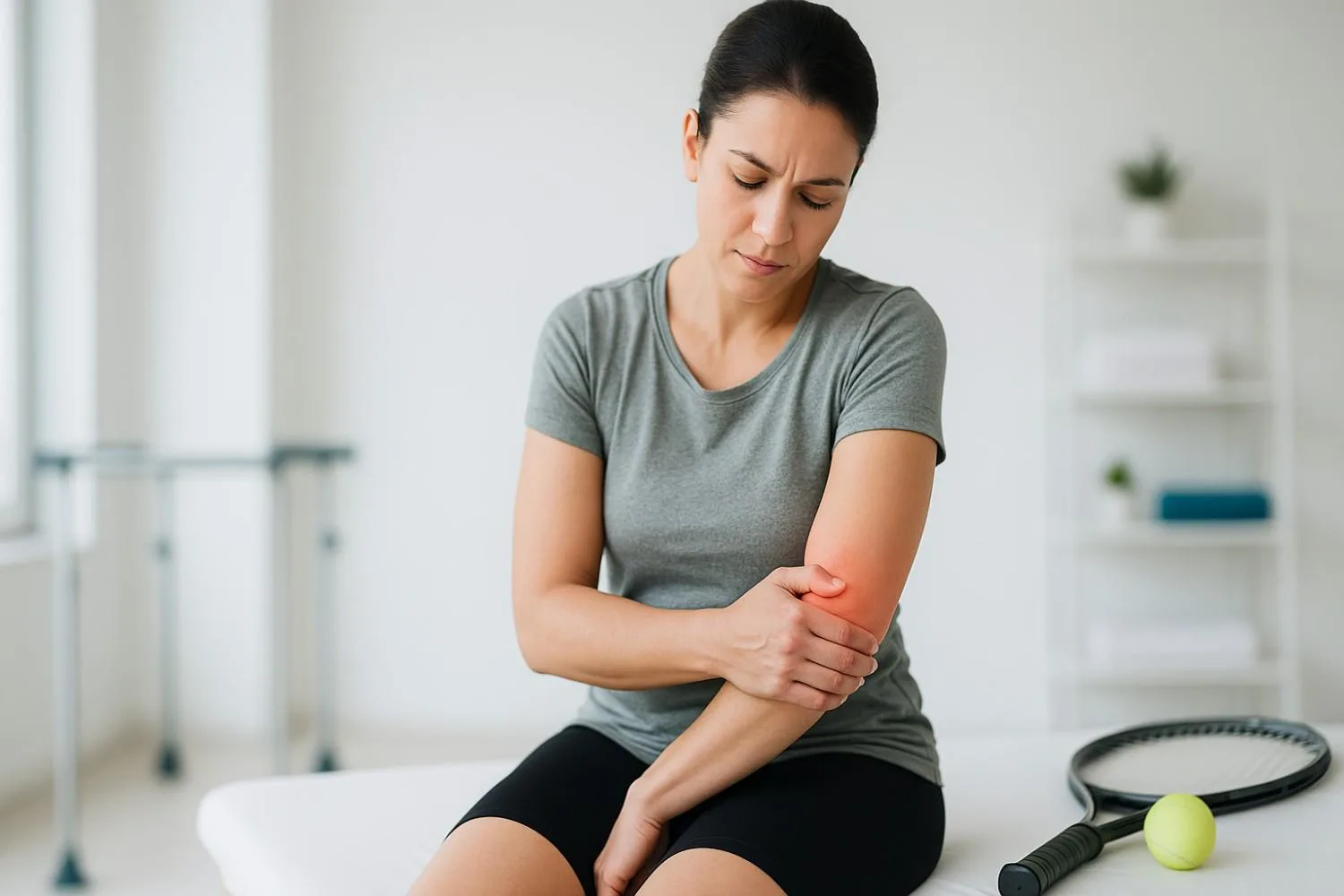
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Early recognition of the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome is crucial for preventing long-term complications. Here are the key signs to watch for:
● Tingling or Numbness:
Especially in the thumb, index, and middle fingers. This may come and go at first and become more persistent over time.
● Hand Weakness:
Difficulty in grasping small objects, dropping things frequently, or clumsiness during fine motor tasks.
● Pain or Discomfort:
Pain may radiate from the wrist up to the arm and even the shoulder.
● Nighttime Worsening:
Symptoms often worsen at night or after repetitive hand use during the day.
If you notice these symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, it’s time to consult a specialist.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the cause of carpal tunnel syndrome is essential for both prevention and treatment. While anyone can develop this condition, certain factors increase your risk:
● Repetitive Hand Movements:
Activities such as typing, playing musical instruments, or using vibrating tools can lead to overuse of the wrist.
● Medical Conditions:
Diabetes, thyroid disorders, and rheumatoid arthritis can increase susceptibility.
● Pregnancy:
Hormonal changes and fluid retention during pregnancy can cause swelling, increasing the risk.
● Wrist Injuries:
Previous fractures, sprains, or trauma to the wrist can affect the tunnel’s structure.
● Genetics:
A narrower carpal tunnel may run in families, predisposing individuals to carpal tunnel syndrome.
Each cause of carpal tunnel syndrome contributes differently, and often multiple factors are involved.
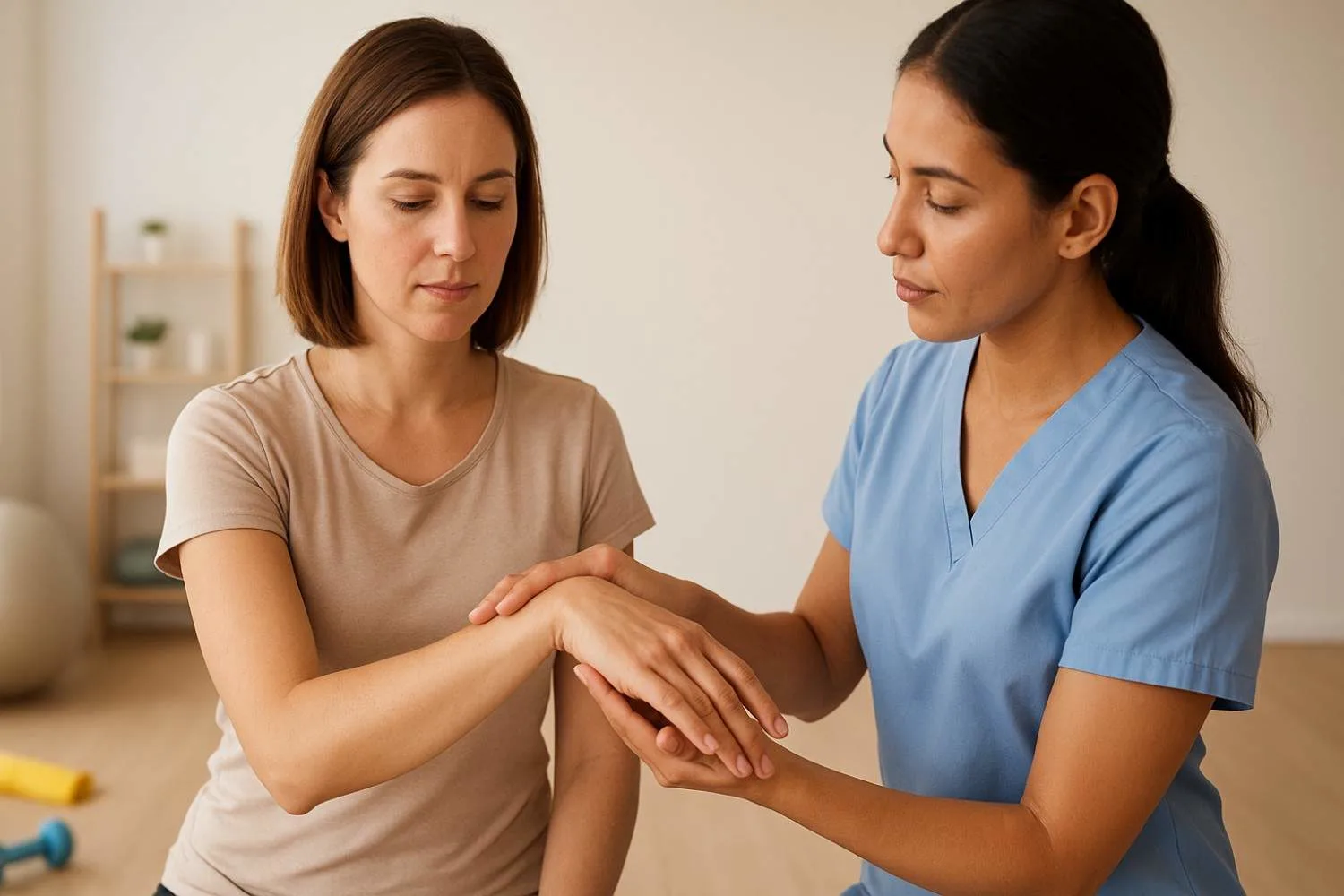
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosis
To confirm a diagnosis, healthcare professionals perform both clinical assessments and diagnostic tests:
● Physical Examination:
Tests like Tinel’s sign and Phalen’s test help determine nerve involvement.
● Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies:
These assess the function of the median nerve and detect the extent of compression.
● Imaging Tests:
Ultrasound or MRI may be used in certain cases to rule out other causes of wrist pain.
Early and accurate diagnosis is key in minimizing the damage caused by carpal tunnel syndrome.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment Options
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
For mild to moderate symptoms, conservative management can be highly effective:
● Wrist Splinting:
Wearing a splint, especially at night, helps keep the wrist in a neutral position and reduces nerve pressure.
● Activity Modification:
Avoiding repetitive tasks or making ergonomic adjustments at work can significantly ease symptoms.
● Medications:
NSAIDs reduce inflammation, while corticosteroid injections can provide temporary relief.
● Physiotherapy:
Targeted exercises improve mobility and strengthen the wrist muscles, relieving pressure on the nerve.
2. Surgical Treatment
If symptoms persist or worsen, surgery may be necessary.
● When Surgery Is Needed:
Severe nerve compression, muscle wasting, or failed non-surgical treatments often indicate surgery.
● Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery:
This involves cutting the ligament pressing on the nerve. Recovery typically takes a few weeks to months, depending on severity.
Choosing the right treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome depends on the duration and intensity of your symptoms.
Prevention Tips for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Preventing carpal tunnel syndrome is possible, especially if you fall into a high-risk group.
● Ergonomic Tools:
Use chairs, keyboards, and workspaces that support neutral wrist positions.
● Stretch Regularly:
Incorporate wrist stretches and finger flexion exercises into your daily routine.
● Frequent Breaks:
Take short breaks when doing repetitive work to avoid overstraining your wrists.
These small steps can help prevent the onset of carpal tunnel syndrome or reduce its severity.
Living with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
If you’ve been diagnosed, managing life with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is entirely possible:
● Long-Term Management:
Regular physiotherapy, ergonomic adjustments, and lifestyle changes go a long way.
● Prognosis:
With appropriate treatment, most people recover well and return to normal activities.
When to See a Doctor for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Don’t ignore persistent symptoms:
● Seek Help If:
Numbness lasts beyond a few days, you experience constant pain, or muscle weakness sets in.
● Early Treatment Matters:
Addressing carpal tunnel syndrome early prevents irreversible nerve damage.
Conclusion
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is more than just a wrist issue-it’s a condition that can affect daily life, especially for pregnant women, office workers, and physiotherapy patients. Understanding what carpal tunnel syndrome is, recognizing the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, knowing the cause of carpal tunnel syndrome, and pursuing the right treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome are all critical to recovery.
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms, don’t wait. Early diagnosis and proper care can prevent long-term complications and restore quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions




















.webp)





.jpg)




































Subscribe now
Get the Latest
Updates With Our Newsletter

Copyright 2026 | Omansh.org
Website designed and developed by PulsePlay Digital

